What are the ergonomic standards for office chairs? A Complete 2026 Guide
Introduction to Ergonomic Standards
In the modern corporate landscape of 2026, the question of what are the ergonomic standards for office chairs has moved from a HR checklist item to a critical component of employee well-being and peak performance. Ergonomics, derived from the Greek words ergon (work) and nomos (natural laws), is the science of designing the workplace to fit the user. When we discuss ergonomic standards for office chairs, we are referring to a set of data-driven specifications that ensure a chair supports the human body in a neutral posture, minimizing strain on the musculoskeletal system.

Table of Contents
- Introduction to Ergonomic Standards
- Global Regulatory Bodies and Standards
- Standard 1: Seat Height and Adjustability
- Standard 2: Seat Depth and Width Requirements
- Standard 3: Lumbar Support and Backrest Geometry
- Standard 4: Armrest Positioning and Flexibility
- Standard 5: Dynamic Movement and Tilt Mechanisms
- Material Safety and Sustainability Standards
- Elevate Your Workspace with Desk One
- The Biological Impact of Ergonomic Non-Compliance
- Choosing the Right Standard for Your Office
- Summary Table of Key Standards
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References and Further Reading
As remote and hybrid work models have stabilized, the demand for furniture that meets international ergonomic standards for office chairs has surged. It is no longer enough for a chair to simply look modern; it must adhere to rigorous mechanical and physiological benchmarks. These standards are developed through extensive anthropometric research—the study of human body measurements—to accommodate the 5th percentile of females to the 95th percentile of males. This ensures that roughly 95% of the population can find a healthy sitting position in a standardized chair.
Global Regulatory Bodies and Standards
Understanding ergonomic standards for office chairs requires a look at the organizations that define them. While specific requirements may vary slightly by region, the core principles of safety, durability, and adjustability remain consistent across the globe.
BIFMA (Business and Institutional Furniture Manufacturers Association)

In North America, BIFMA is the gold standard. Specifically, the ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 standard outlines the minimum requirements for safety and durability for general-purpose office chairs. Furthermore, BIFMA G1-2013 provides specialized guidelines purely for ergonomics, focusing on the interface between the human body and the chair.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
ISO 9241-5 is a globally recognized standard for the ergonomic requirements of office work with visual display terminals (VDTs). It emphasizes the importance of the user being able to change postures frequently, a concept known as dynamic sitting.
EN 1335 (European Standards)
In Europe, the EN 1335 series specifies dimensions and safety requirements. This standard is particularly strict regarding the ranges of adjustability, ensuring that chairs sold in the EU can cater to a diverse demographic of body types.
Standard 1: Seat Height and Adjustability
The most fundamental aspect of ergonomic standards for office chairs is adjustable seat height. A chair that is too high puts pressure on the underside of the thighs, restricting blood flow. A chair that is too low forces the pelvis to tilt backward, flattening the natural curve of the lower back.
According to current ergonomic standards for office chairs, the seat height should be adjustable within a range that allows the user's feet to rest flat on the floor while their thighs are parallel to the ground, and their hips are slightly higher than their knees. Typically, this translates to a range of 15 to 22 inches (38 to 56 cm) from the floor. The adjustment mechanism must be easy to operate from a seated position, usually utilizing a pneumatic gas lift that meets Class 4 durability ratings.
Standard 2: Seat Depth and Width Requirements
Seat depth is a frequently overlooked but vital part of ergonomic standards for office chairs. If the seat is too deep, it will press against the back of the knees (the popliteal fold), causing the user to slouch forward and lose the support of the backrest. If it is too shallow, the thighs aren't properly supported, leading to instability.
The standard requirement for seat depth is a range of 15 to 17 inches, often with a "slider" mechanism that allows for 2 or more inches of adjustment. A crucial ergonomic rule is that there should be a 2 to 4-inch gap (approximately 3 fingers) between the edge of the seat and the back of the knees. Regarding width, ergonomic standards for office chairs suggest a minimum of 17 to 20 inches to accommodate different hip sizes comfortably without the user feeling restricted by the armrests.
Standard 3: Lumbar Support and Backrest Geometry
The human spine has a natural inward curve at the lower back (the lordotic curve). Sitting for long periods without support causes this curve to collapse, leading to disc compression and muscle fatigue. Therefore, integrated and adjustable lumbar support is a non-negotiable feature in ergonomic standards for office chairs.
Standard requirements state that the lumbar support should be adjustable both in height and depth. The height adjustment allows the user to position the curve of the backrest precisely in the small of their back. High-quality ergonomic standards for office chairs in 2026 also emphasize backrest height, which should be between 12 and 19 inches wide and provide support for the thoracic region (middle back) as well as the lumbar region.
Standard 4: Armrest Positioning and Flexibility
Armrests are essential for reducing the load on the neck and shoulders. However, if they are poorly positioned, they can prevent the user from pulling the chair close enough to the desk, leading to "reaching" and strained traps. Modern ergonomic standards for office chairs advocate for 3D or 4D armrests.
The standards dictate that armrests should be height-adjustable (usually between 7 and 11 inches above the seat) to allow the elbows to rest at a 90-degree angle. Furthermore, they should be adjustable in width (moving closer or further from the torso) and pivotable. This flexibility ensures that the weight of the arms is supported whether the user is typing, using a mouse, or reading.
Standard 5: Dynamic Movement and Tilt Mechanisms
Static sitting is the enemy of health. Recent updates to ergonomic standards for office chairs focus heavily on tilt mechanisms and tension control. A chair should allow for a reclining motion that keeps the feet on the floor while opening the hip angle, which improves circulation and reduces pressure on the spinal discs.
Synchro-tilt is the preferred mechanism under ergonomic standards for office chairs. This mechanism allows the backrest to recline at a higher ratio than the seat (usually 2:1), preventing the "rocking chair" effect and maintaining proper posture throughout the movement. Tension control is also required so that users of different weights can recline with the same level of effort and support.
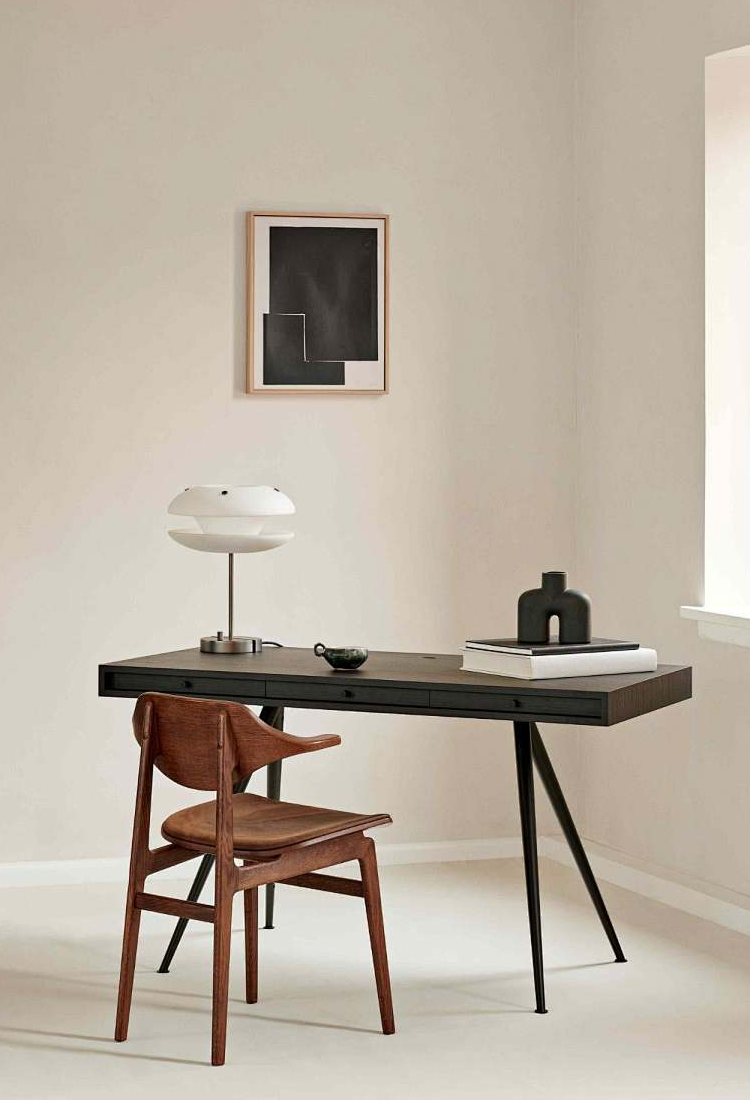
Welcome to Desk One – Your Gateway to Elevating Workspaces!
Discover a world where office furniture transcends the ordinary, where innovation meets functionality, and where your workspace becomes an oasis of productivity and style. At Desk One, we're not just a furniture destination; we're your partners in creating inspiring and efficient work environments.
Located in the heart of Queensland, with bases in Willawong, we've earned our stripes as a trusted wholesale supplier of top-tier office furniture. While our specialty lies in crafting premium office desks and ergonomic chairs, we offer a vast selection of furniture solutions designed to cater to the unique needs of modern offices. All our chairs are designed with ergonomic standards for office chairs at their core.
Featured Ergonomic Solutions



Explore our full range and learn more about our commitment to quality at our Queensland showroom or online.
Material Safety and Sustainability Standards
Beyond dimensions and mechanics, ergonomic standards for office chairs also cover the chemistry of the materials used. The GREENGUARD Certification is often cited in these standards, ensuring that the chair does not emit harmful Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) into the office air.
Furthermore, the breathability of the material is an ergonomic factor. High-performance mesh, as seen in the Desk One Apex Ergo series, allows for heat dissipation, keeping the body temperature regulated. This is crucial for comfort during long shifts, as excessive heat can lead to restlessness and poor posture. Standard ergonomic standards for office chairs also require that fabrics be fire-retardant and pass friction tests to prevent the user from sliding out of the seat.
The Biological Impact of Ergonomic Non-Compliance
When a workplace ignores ergonomic standards for office chairs, the biological cost is high. Prolonged sitting in a non-standard chair leads to Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs), including carpal tunnel syndrome, tension neck syndrome, and chronic lower back pain. These conditions are not just painful; they are the leading cause of absenteeism and reduced productivity globally.
By adhering to ergonomic standards for office chairs, companies can reduce the mechanical load on the spine by up to 40%. Proper lumbar support helps maintain the oxygenation of spinal discs, while adjustable armrests prevent the "shrugging" motion that leads to tension headaches. Investing in standardized ergonomic seating is essentially a preventative healthcare strategy for the office.
Choosing the Right Standard for Your Office
Selecting a chair that meets ergonomic standards for office chairs can be overwhelming. A helpful tip is to look for certifications such as the AFRDI (Australian Furnishing Research and Development Institute) "Blue Tick" for those in the Australian market. This certification guarantees that the chair has been tested for a 40-hour work week and meets strict ergonomic and structural requirements.
When evaluating chairs like the Desk One Ergo Elite, ask for the technical specification sheet. Ensure that the adjustability ranges match the anthropometric needs of your staff. Remember, a chair is only ergonomic if it fits the person sitting in it. A high-end chair that doesn't adjust to a petite user's height is essentially an unergonomic chair for that individual.
Summary Table of Key Standards
| Feature | Ergonomic Standard Requirement | Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Seat Height | 15" - 22" (Adjustable) | Reduces thigh pressure; aids circulation |
| Seat Depth | 15" - 17" with 2" slider | Prevents knee pressure; ensures back support |
| Lumbar Support | Height and Depth adjustable | Maintains spinal lordotic curve |
| Armrests | 3D or 4D adjustability | Relieves neck and shoulder tension |
| Backrest Tilt | Synchro-tilt (minimum 100° - 110°) | Encourages dynamic movement |
| Stability | 5-prong base with casters | Prevents tipping and allows mobility |
Frequently Asked Questions
With the rise of sedentary work and the long-term health implications of sitting, these standards ensure that office furniture supports the body's natural anatomy, reducing the risk of chronic pain and increasing overall work efficiency.
A standard chair often has fixed components. An ergonomic chair following modern standards must have at least five points of adjustment: seat height, seat depth, lumbar support, backrest tilt, and armrest height.
Yes, as long as it provides sufficient tension and adjustable lumbar support. Mesh is often preferred in ergonomic standards for office chairs for its breathability and ability to contour to the user's back.
Under BIFMA and AFRDI standards, high-quality chairs are tested to last 7-10 years. However, the pneumatic lift or padding may need checking every 5 years to ensure they still meet the original ergonomic benchmarks.
Article Summary: Ergonomic standards for office chairs are critical guidelines that dictate the dimensions, adjustability, and safety of seating. By prioritizing features like adjustable seat depth, synchro-tilt, and lumbar support, you protect your physical health and boost workplace productivity. Brands like Desk One specialize in providing solutions that meet these high-level specifications.
References and Further Reading
- Business and Institutional Furniture Manufacturers Association (BIFMA). (2023). ANSI/BIFMA X5.1-2017(R2022) General-Purpose Office Chairs.
- International Organization for Standardization. (2017). ISO 9241-5: Ergonomic requirements for office work with visual display terminals.